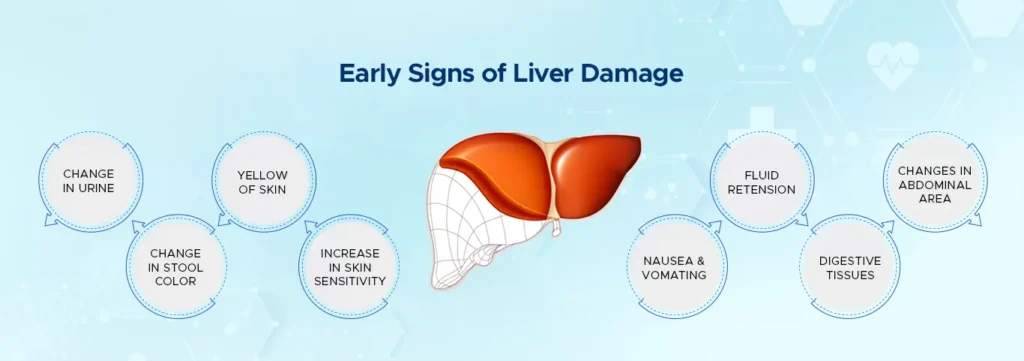
Daily life overloads the liver leading to poor health and disease.
Liver is the largest gland in the human body, which is responsible for hundreds of critical functions to keep the body free from toxins and harmful substances. Besides fighting infections and illnesses, liver is responsible for removing toxins, such as alcohol, from the body and controls cholesterol levels. It produces a special liquid, known as bile, which helps break down fat and boosts digestion. Liver also helps your body fight infections by removing bacteria from the blood. Liver is the only organ in the body that can easily replace damaged cells, but if excessive cells are lost, the liver may not be able to function properly, giving rise to various Liver diseases. Liver can be damaged in many ways, and may or may not show any early symptoms:
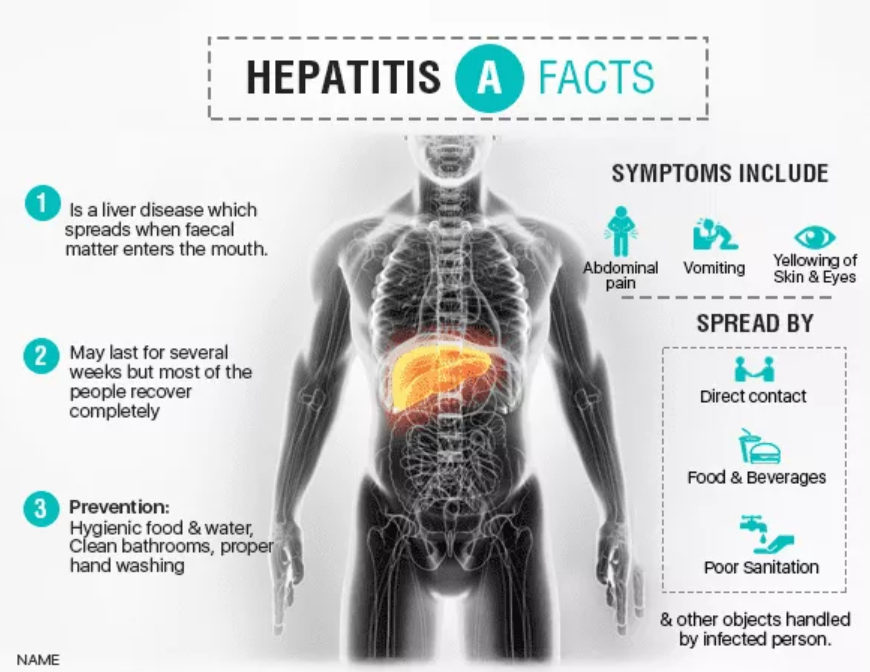
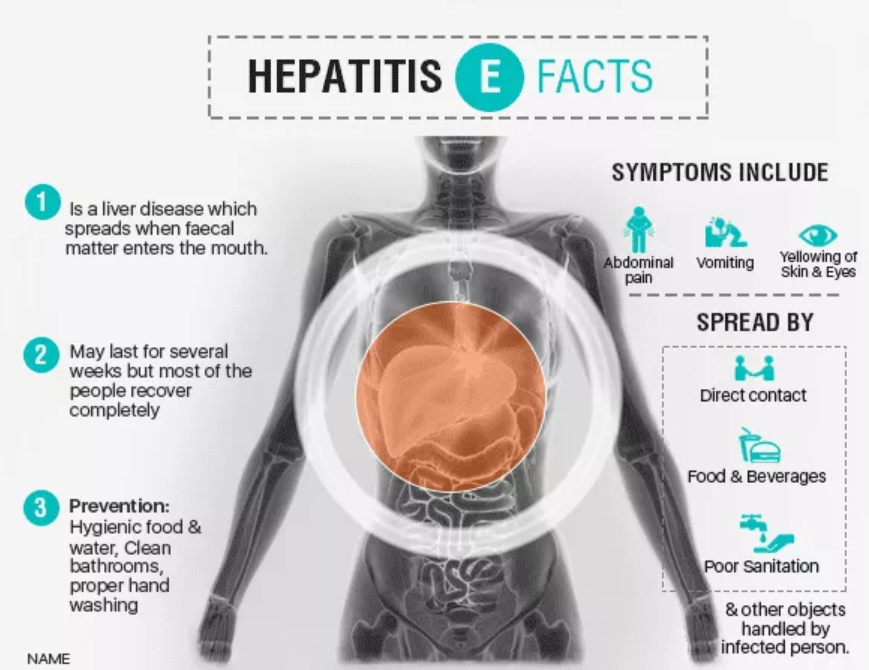
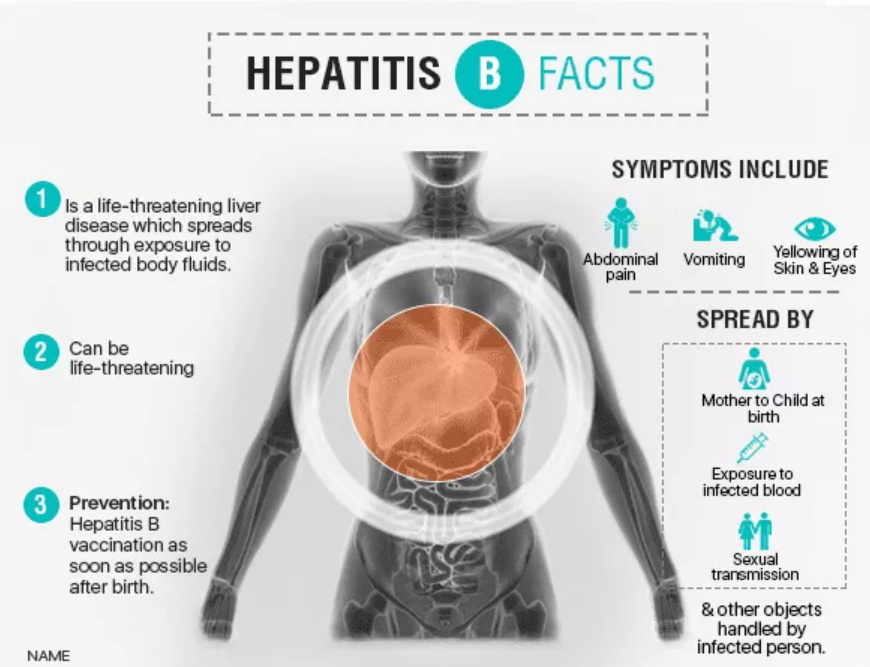
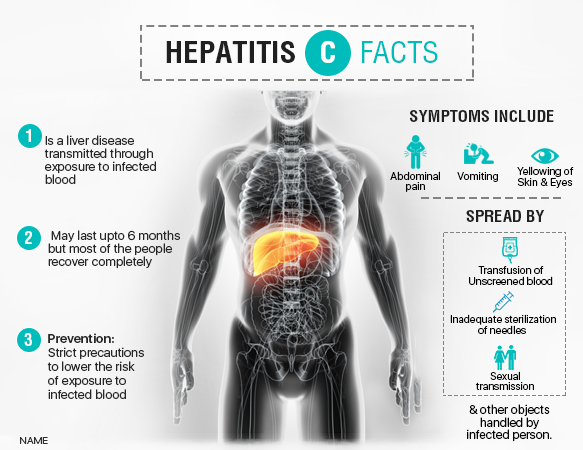
- Inflammation of Cells, giving rise to Hepatitis
- Obstruction in the production of Bile, causing diseases such as Cholestasis
- Accumulation of Cholesterol or Triglycerides, causing Steatosis
- Hindrance in the flow of blood to the liver, where the liver breaks down the blood and creates necessary nutrients for the body.
- Liver tissue damage due to harmful chemicals, drugs & medications
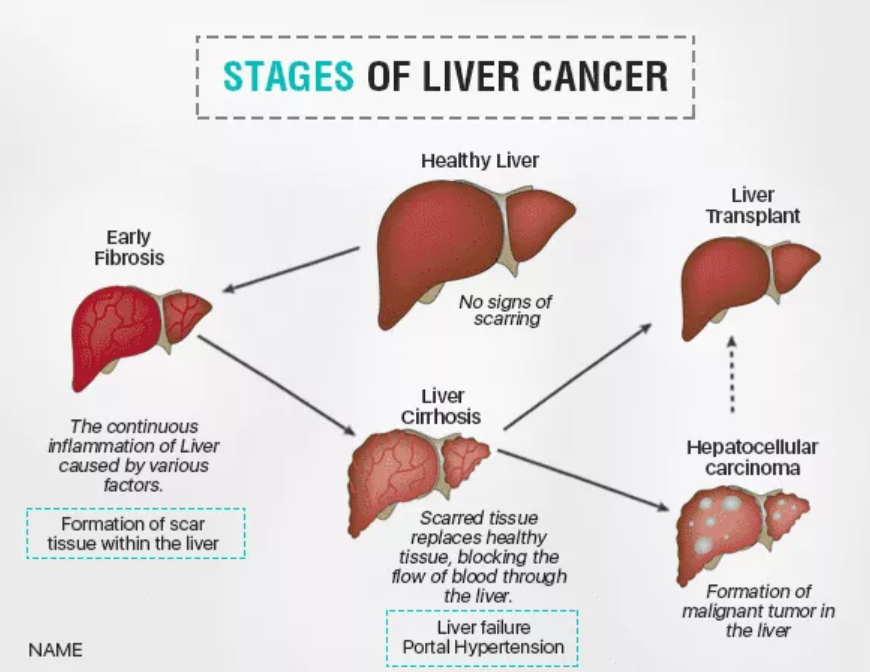
- Infiltration of abnormal cells, such as Cancer Cells